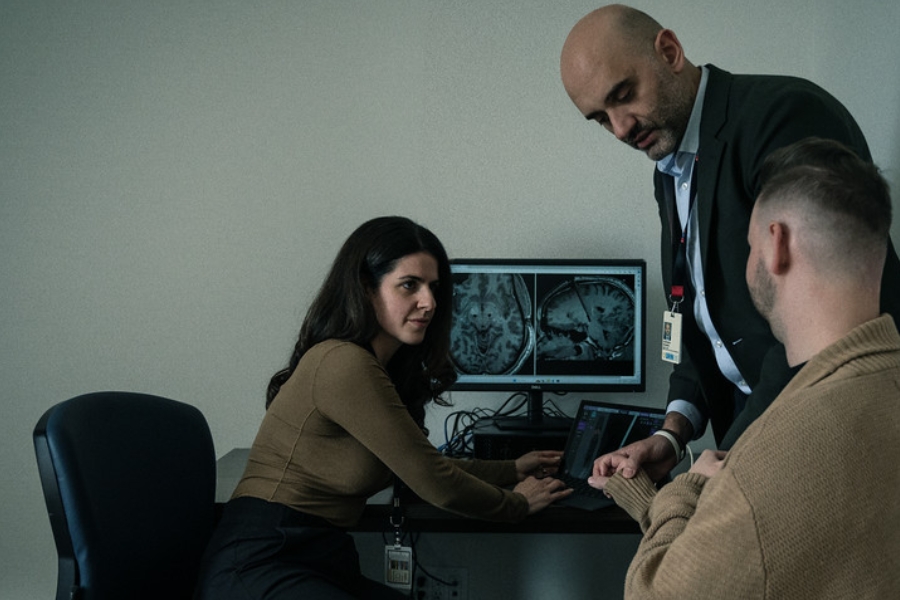
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive brain disease that targets the body’s nervous system. PD occurs due to a shift in brain chemistry. The loss of neurons that produce dopamine in the basal ganglia, an area of the brain which controls movement, leads to slowed movements and tremor symptoms. There is no cure for PD, but therapies and medications can help reduce negative symptoms associated with the illness.
To the detriment of the patient, these symptoms get worse over time and can greatly reduce well-being and quality of life. When medications do not help manage these symptoms effectively, Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) can be leveraged to minimize symptoms and side-effects.
Here are 6 key things to know about Deep Brain Stimulation and its role in treating Parkinson’s disease:
1. Surgical Procedure
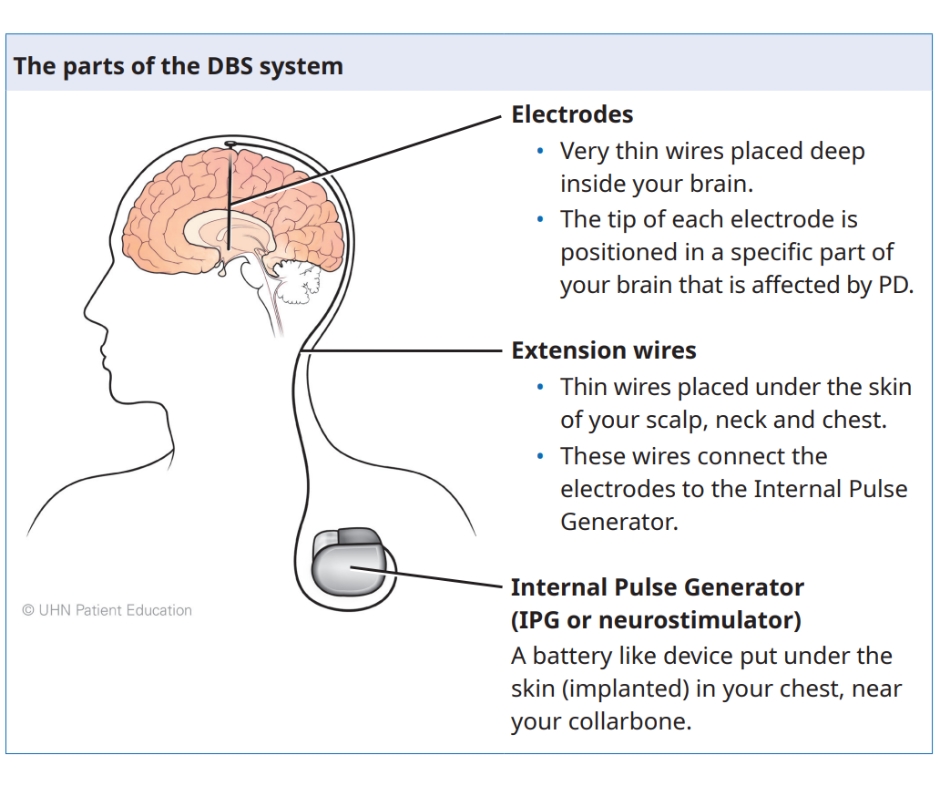
DBS involves the surgical implantation of three DBS parts in your body. These parts are electrodes, extension wires and an internal pulse generator. These electrodes are connected to the pulse generator, a battery like device placed under the skin in your chest.
2. Targeted Brain Regions
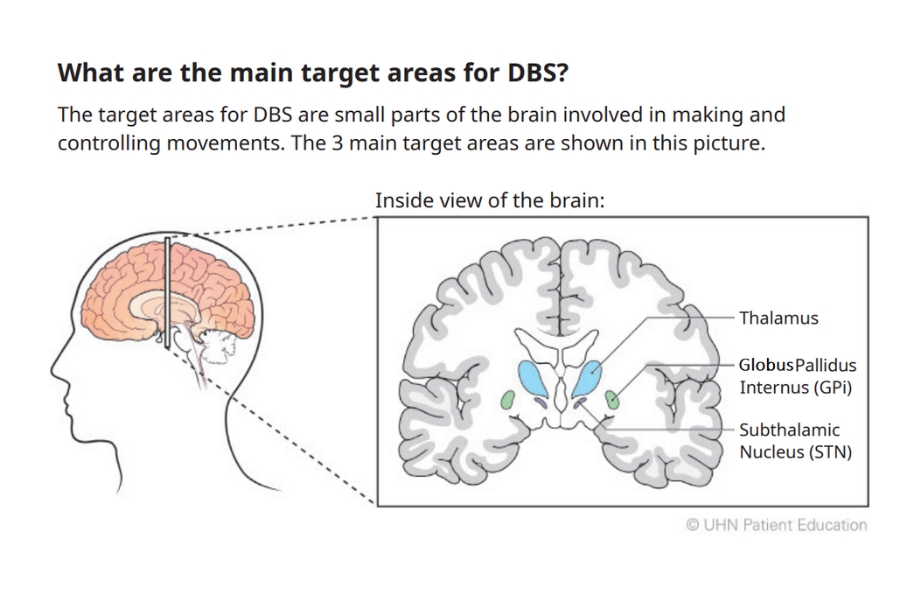
In this treatment, a mild electrical current is used to stimulate deep areas of the brain associated with movement: the subthalamic nucleus (STN), the globus pallidus internus (GPi), and/or the thalamus. Stimulation of these regions helps regulate abnormal signaling patterns associated with PD, reducing negative side effects.
3. Symptom Management
DBS is highly effective in managing the motor symptoms of PD, including tremors, rigidity, and slow movements. DBS may also help if you have problems related to PD medications, such as frequent or sudden ‘OFF’ periods when medication ceases to manage movement symptoms.
4. Adjustable Stimulation
The level of electrical stimulation is personally tailored to meet the individual’s specific needs, resulting in a more personalized approach to symptom management.
5. Reduction of Medication
DBS often enables patients to reduce the amount of medication they take, relieving medication-related side effects. Medication may still be required, but at a lower dose, to accompany the benefits of the electrical stimulation.
6. Improvement in Quality of Life

Individuals with PD who undergo DBS experience significant improvements in their well-being and quality of life. Click here to read about how UHN helped Fabio get back to doing what he loves.

No one ever changed the world on their own but when the bright minds at UHN work together with donors we can redefine the world of health care together.


