The findings were published in the Journal of Neurotrauma.
Using a clustergram analysis to visualize potential patterns between patients and symptoms, researchers analyzed data collected from 110 patients suffering from PCS. The results of the analysis yielded new insights about the condition that will help health practitioners better inform and treat PCS sufferers. The study found that:
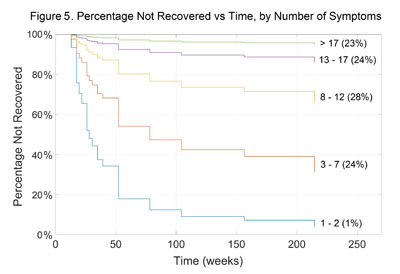
- The number of symptoms PCS sufferers experienced predicted whether or not they would recover. For example, patients with one or two symptoms were more likely to recover more quickly than those with 10 or more symptoms (figure 5).
- Individuals with persistent concussion symptoms who resumed sport despite recommendations not to, were more likely not to recover from PCS.
- Relationships appear to exist between certain PCS symptoms. For instance, PCS sufferers who reported experiencing anxiety also reported depression, two symptoms that appeared to go hand in hand. More research is needed to better understand this relationship, but it could indicate that the brain regions responsible for these symptoms are near each other and were injured together.
- The clustergram showed two distinct groups of symptoms among the PCS sufferers with one group of symptoms being reported much more often than the other. Furthermore, symptoms from the group that were observed less frequently weren’t present unless those from the group of more common symptoms were also present, indicating a predictable order of symptom expression.
- Finally, patients with symptoms that lasted for more than three years did not recover fully from PCS. This is the first study to indicate there could be a definite period for PCS after which recovery is unlikely, but more research is needed from a larger sample size to determine if this holds true.
“These findings flag that the presence of multiple symptoms with PCS may indicate a prolonged illness,” says Krembil Neurosurgeon Dr. Charles Tator who led the study. “Although more research is needed, based on these findings I would encourage health practitioners to pay attention to the multiplicity of symptoms in PCS patients and vigorously treat as many of them as possible to increase chances of recovery.”
According to existing research, PCS affects anywhere from five to 43 per cent of concussed individuals, people who would otherwise fully recover within the first three months of sustaining a concussion. Little is known about the exact cause of PCS, and it is also unknown whether PCS is a predictor of chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) a progressive neurodegenerative disease that has been linked to multiple concussions.
“There is such a wide range of recovery among PCS sufferers that further investigation is necessary to better understand the condition,” says Tator. “Once we can better characterize this phase of concussion injury, we hope that will help us determine whether there is also a link with CTE.”
The research team will continue to follow the study participants for at least 10 years to note any changes in their symptoms.
Clustergram analysis is part of machine learning technology, an emerging field in healthcare that provides mathematical support to analyze large amounts of information and data in order to identify significant patterns in a wide variety of diseases. In the present study, many of the findings were only apparent by using machine learning.
